Floating roofs are used on storage tanks to minimize vapor space between the top of the tank and the level of the liquid, typically a petroleum-based product, inside the tank. Per the External floating roof tank Wikipedia entry:
In this 3:40 YouTube video, How to Increase Safety with Continuous Surveillance of Floating Roof Movements, Emerson’s Ulf Johannesson explains how wired or wireless radar level measurement technologies are used to monitor the location of the roof in relationship to the level of the liquid. By continuously monitoring the roof location at different points on the roof, issues such as a stuck or tilted roof condition can be discovered early and corrected before an abnormal situation occurs and worsens.The roof rises and falls with the liquid level in the tank. As opposed to a fixed roof tank there is no vapor space (ullage) in the floating roof tank (except for very low liquid level situations). In principle, this eliminates breathing losses and greatly reduces the evaporative loss of the stored liquid. There is a rim seal system between the tank shell and roof to reduce rim evaporation.
Ulf opens highlighting some of the common issues that can occur with floating roof tanks. These include wind-induced roof tilt, imbalance causes by rain or snow, rim seal friction, pontoon or deck leaks, tank wall abnormalities, roof access ladder binding and block roof drains.
The traditional way to monitor for these conditions was visual inspections by tank farm personnel. This practice placed personnel in hazardous locations and provided only intermittent monitoring which could miss the early stages of a developing problem.
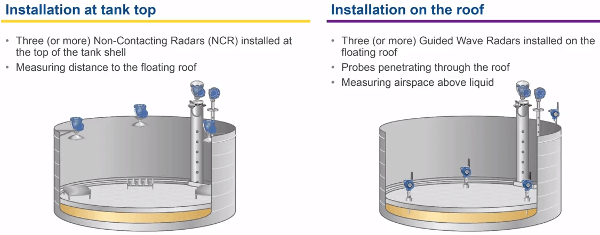
Ulf highlights two approaches for monitoring floating roof level and tilt conditions. The wired approach uses non-contacting radars mounted at the top of the tank shell. Spacing 3 or more non-contacting radar measurement instruments around the tank provides a measurement from the top of the tank shell down to the floating roof level inside the tank.
The second approach is to install three or more wireless guided wave radar measurement instruments in which the probes penetrate through the roof down into the tank to measure the airspace above the liquid. In both cases, a separate reading is used to measure the liquid level as shown in the picture below. Differences between the measurements indicate a tilt, stuck roof or improper draining condition.
You can connect and interact with other tank gauging and level measurement experts in the Tank Gauging and Level groups in the Emerson Exchange 365 community.